How Long Does It Take Cervical Cancer To Spread
Cervical cancer
Cancer - cervix; Cervical cancer - HPV; Cervical cancer - dysplasia
Cervical cancer is cancer that starts in the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina.
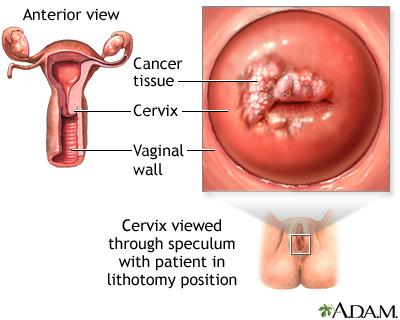
The development of cervical cancer is gradual and begins as a pre-cancerous status called dysplasia. Information technology is usually a slow-growing cancer and if defenseless early can exist successfully treated. Routine Pap smears can detect early changes in the cells of the cervix allowing cervical cancer to be diagnosed early on.
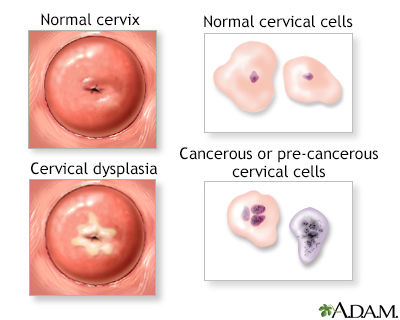
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is the presence of abnormal cells on the surface of the neck. A Pap smear and colposcopy are two of the procedures performed to monitor the cells and appearance of the cervix.
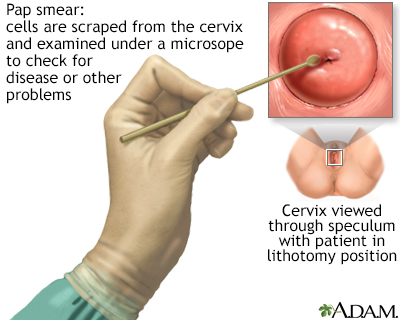
A Pap examination is a uncomplicated, relatively inexpensive procedure that can hands detect malignant or precancerous weather.
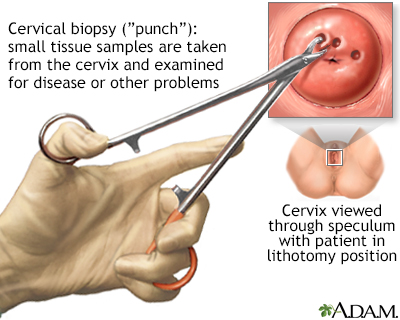
In a cervical punch biopsy, the cervix may be stained with iodine solution in order to see abnormalities better. These areas of tissue are and so sampled and examined.
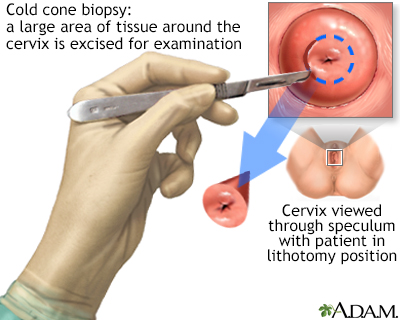
The common cold cone biopsy is a surgical process requiring general anesthesia and is indicated by the presence of precancerous changes in the cervix.
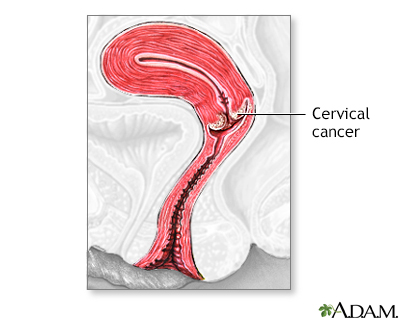
Cervical cancer is the tertiary near common blazon of cancer in women. Approximately ii% to 3% of all women over historic period 40 years will develop some course of cervical cancer.
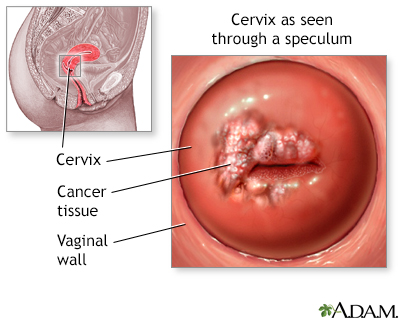
An instrument called a speculum holds the walls of the vagina open then that the cervix may exist viewed and a swab of cells obtained for analysis.
Causes
Worldwide, cervical cancer is the tertiary most mutual blazon of cancer in women. It is much less common in the United States because of the routine use of Pap smears.
Cervical cancer starts in the cells on the surface of the neck. There are two types of cells on the surface of the neck, squamous and columnar (gland cells). Most cervical cancers are from squamous cells.
Cervical cancer commonly develops slowly. It starts equally a precancerous condition called dysplasia. This status tin can exist detected past a Pap smear and is virtually 100% treatable. It can take years for dysplasia to develop into cervical cancer. Most women who are diagnosed with cervical cancer today have not had regular Pap smears, or they have non followed up on abnormal Pap smear results.
Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common virus that is spread through skin-to-pare contact and likewise by sexual intercourse. There are many different types (strains) of HPV. Some strains lead to cervical as well as other cancers. Other strains can cause genital warts. Others do not crusade any problems at all.
A woman'south sexual habits and patterns can increase her risk for developing cervical cancer. Risky sexual practices include:
- Having sex at an early age
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Having a partner or many partners who take role in loftier-hazard sexual activities
Other gamble factors for cervical cancer include:
- Non getting the HPV vaccine
- Being economically disadvantaged
- Having a mother who took the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy in the early 1960s to preclude miscarriage
- Having a weakened immune system
Worldwide, cervical cancer is the third most mutual type of cancer in women. Luckily, it'south much less mutual in the The states due to women receiving recommended routine Pap smears, the test designed to discover cervical cancer sometimes even before abnormal cells turn to cancer. Cervical cancer starts in the cells on the surface of the cervix, the lower portion of the uterus. At that place are two types of cells on the surface of the cervix, squamous and columnar. Most cervical cancers come from these squamous cells. The cancer usually starts very slowly every bit a condition called dysplasia. This precancerous condition tin can be detected past Pap smear and is 100% treatable. Undetected, precancerous changes tin develop into cervical cancer and spread to the bladder, intestines, lungs, and liver. It can accept years for these precancerous changes to turn into cervical cancer. Withal, patients with cervical cancer practise not normally have problems until the cancer is avant-garde and has spread. About of the time, early cervical cancer has no symptoms. Symptoms of avant-garde cancer may include back pain, bone fractures, fatigue, heavy vaginal bleeding, urine leakage, leg pain, loss of appetite, and pelvic pain. If afterward having a Pap smear, the physician finds abnormal changes on the cervix, a colposcopy can be ordered. Using a lite and a low-powered microscope, the doc will view the cervix under magnification. The doctor may remove pieces of tissue, called a biopsy, and send the sample to a laboratory for testing. If the woman is diagnosed with cervical cancer, the doctor will order more than tests to determine how far the cancer has spread. This is chosen Staging. Treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer, the size and shape of the tumor, the adult female's age and full general health, and her want to accept children in the future. Early on cervical cancer can be treated with surgery just to remove abnormal tissue, freeze abnormal cells, or burn abnormal tissue. Treatment for more advanced cervical cancer may include radical hysterectomy, removal of the uterus and much of the surrounding tissue, including lymph nodes and the upper part of the vagina. Radiations may be used to treat cancer that has spread beyond the pelvis, or if cancer returns. The woman may besides have chemotherapy to kill cancer cells. About all cervical cancers are caused by man papilloma virus, or HPV. This common virus is spread through sexual intercourse. HPV vaccines tin forbid infection against the two types of HPV responsible for virtually lxx% of cervical cancer. Practicing safe sex also reduces the risk of getting HPV. Just, go along in listen virtually women diagnosed with cervical cancer take not had their regular Pap smears. Considering Pap smears can find precancerous growths that are 100% treatable, it's very important for women to get Pap smears at regular intervals.
Symptoms
Most of the fourth dimension, early on cervical cancer has no symptoms. Symptoms that may occur include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods, afterwards intercourse, or afterwards menopause
- Vaginal discharge that does not stop, and may exist pale, watery, pink, brown, bloody, or foul-smelling
- Periods that become heavier and last longer than usual
Cervical cancer may spread to the vagina, lymph nodes, bladder, intestines, lungs, bones, and liver. Frequently, there are no issues or symptoms until the cancer is advanced and has spread. Symptoms of advanced cervical cancer may include:
- Back pain
- Bone pain or fractures
- Fatigue
- Leaking of urine or feces from the vagina
- Leg pain
- Loss of ambition
- Pelvic pain
- Single swollen leg
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
Precancerous changes of the cervix and cervical cancer cannot be seen with the naked eye. Special tests and tools are needed to spot such atmospheric condition:
- A Pap smear screens for precancers and cancer, but does not make a terminal diagnosis.
- Depending on your historic period, the human papillomavirus (HPV) Deoxyribonucleic acid test may be done forth with a Pap exam. Or it may exist used after a adult female has had an abnormal Pap examination effect. It may also be used equally the first test. Talk to your health care provider well-nigh which examination or tests are right for you lot.
- If abnormal changes are found, the cervix is usually examined nether magnification. This procedure is called colposcopy. Pieces of tissue might be removed (biopsied) during this procedure. This tissue is then sent to a lab for examination.
- A procedure called a cone biopsy may also be done. This is a procedure that removes a cone-shaped wedge from the front of the cervix.
If cervical cancer is diagnosed, the provider will order more than tests. These help determine how far the cancer has spread. This is called staging. Tests may include:
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the pelvis
- Cystoscopy
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- MRI of the pelvis
- PET scan
If you're a woman 21 or over, information technology'southward important to begin getting regular pelvic examinations to take charge of your health. An important role of this pelvic exam may include a test, called a Pap smear, to find the ofttimes life-threatening disease, cervical cancer, even before it starts. And here'southward the key, cervical cells become abnormal years before they turn to cancer. That gives an excellent window of opportunity. Then, what is a Pap smear? A Pap smear is a microscopic exam of cells scraped from the opening of the cervix. The neck is the lower role of the uterus, or womb, that opens at the pinnacle of the vagina. The test looks for cervical cancer or abnormal cells. Virtually cervical cancers can be found, and treated early on, or even before they start, if women have routine Pap smears and pelvic examinations. For this test, you will lie on a table and place your feet in stirrups. The physician will insert an instrument called a speculum into the vagina and open information technology slightly to see inside the vaginal canal. Cells are gently scraped from the cervix area, and sent to a lab for examination. When a Pap smear shows aberrant changes, you will need further testing. The next step depends on the results of the Pap smear, and on your previous history of Pap smears, and risk factors you may have for cervical cancer. You may demand a biopsy using a light and a low-powered microscope, called colposcopy. You lot may also need a examination to bank check for infection with human being papilloma virus, or HPV, which tin can crusade cervical cancer. If you are diagnosed with cervical cancer, the doctor volition gild more tests to determine how you should be treated, and how far the cancer has spread. This is chosen staging. Handling will depend on the stage of the cancer, the size and shape of the tumor, your age and general health, and your want to take children in the hereafter. Early on cervical cancer can exist treated with surgery to remove the abnormal tissue, or freeze abnormal cells, or fire aberrant tissue. Treatment for more advanced cervical cancer may include radical hysterectomy, removal of the uterus and much of the surrounding tissue, including lymph nodes and the upper function of the vagina. Radiation may be used to care for cancer that has spread beyond the pelvis, or if cancer returns. The woman may as well have chemotherapy to kill the cancer if the cervical cancer's advanced. The Pap smear exam is not 100% accurate and cervical cancer may exist missed in a pocket-size number of cases. Fortunately, cervical cancer develops very slowly in nearly women and follow-up Pap smears should identify worrisome changes in enough of fourth dimension for handling. Make sure your md knows near all the medicines you lot are taking. Some, including estrogen and progestins, may impact the result of your Pap smear. Pap smears tin be a wonderful, life saving tool.
Treatment
Treatment of cervical cancer depends on:
- The stage of the cancer
- The size and shape of the tumor
- The woman'due south historic period and general health
- Her desire to have children in the future
Early on cervical cancer can be cured past removing or destroying the precancerous or cancerous tissue. This is why routine Pap smears are and then important to prevent cervical cancer, or grab it at an early on stage. There are surgical means to exercise this without removing the uterus or seriously damaging the cervix, and so that a woman can still take children in the futurity.
Types of surgery for cervical precancer, and on occasion, very minor early cervical cancer include:
- Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) -- uses electricity to remove aberrant tissue.
- Cryotherapy -- freezes abnormal cells.
- Laser therapy -- uses light to burn aberrant tissue.
- Hysterectomy may be required for women with precancer who take undergone multiple LEEP procedures, or who are not interested in further childbearing.
Handling for more advanced cervical cancer may include:
- Radical hysterectomy, which removes the uterus and much of the surrounding tissues, including lymph nodes and the upper part of the vagina. This is more ofttimes performed on younger, healthier women with small tumors.
- Radiation therapy, along with low dose chemotherapy, is more often used for women with tumors too big for radical hysterectomy or women who are not good candidates for surgery.
- Pelvic exenteration, an farthermost type of surgery in which all of the organs of the pelvis, including the bladder and rectum, are removed.
Radiation may also be used to care for cancer that has returned.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer. It may be given alone or with surgery or radiation.
Support Groups
You lot can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have mutual experiences and problems can help you not experience alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well the person does depends on many things, including:
- Type of cervical cancer
- Stage of cancer (how far it has spread)
- Historic period and general wellness
- If the cancer comes dorsum later treatment
Precancerous weather tin be completely cured when followed upwardly and treated properly. Nigh women are alive in v years (5-year survival rate) for cancer that has spread to the inside of the neck walls but not exterior the cervix area. The 5-yr survival rate falls equally the cancer spreads outside the walls of the neck into other areas.
Possible Complications
Complications can include:
- Adventure of the cancer coming back in women who have treatment to salvage the uterus
- Problems with sexual, bowel, and float function after surgery or radiation
When to Contact a Medical Professional person
Contact your provider if yous:
- Take not had regular Pap smears
- Have abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
Prevention
Cervical cancer can be prevented past doing the following:
- Get the HPV vaccine. The vaccine prevents about types of HPV infection that cause cervical cancer. Your provider can tell you if the vaccine is right for you lot.
- Practice safer sex. Using condoms during sex reduces the take chances for HPV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Limit the number of sexual partners yous have. Avoid partners who are active in high-risk sexual behaviors.
- Become Pap smears every bit oft every bit your provider recommends. Pap smears can aid notice early changes, which tin be treated before they plow into cervical cancer.
- Become the HPV test if recommended by your provider. It can be used along with the Pap test to screen for cervical cancer in women 30 years and older.
- If you fume, quit. Smoking increases your chance of getting cervical cancer.
References
Centers for Affliction Command and Prevention website. Human being papillomavirus (HPV) schedule and dosing.
National Cancer Found website. Cervical cancer treatment (PDQ) - wellness professional version.
Salcedo MP, Phoolcharoen N, Schmeler KM. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the lower genital tract (neck, vagina, vulva): etiology, screening, diagnosis, direction. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 29.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Cervical cancer: screening.
Version Info
Terminal reviewed on: 1/1/2022
Reviewed by: Howard Goodman, Doc, Gynecologic Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Enquiry Institute, West Palm Embankment, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 09/13/2022.

Source: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/cervical-cancer
Posted by: johnsonbleanto1988.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Long Does It Take Cervical Cancer To Spread"
Post a Comment